What is Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) and how to fix it?
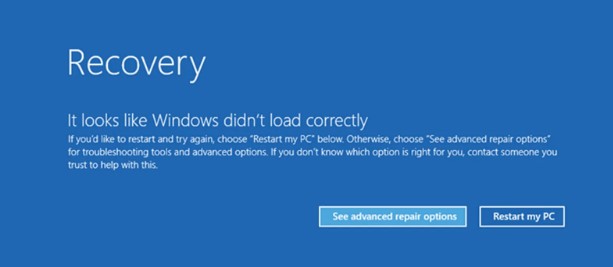
Hey there, If you’ve been keeping up with recent tech news, you might have heard about the global Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) phenomenon that recently swept through computers everywhere. It was like a tech apocalypse for a moment computers crashing, work coming to a stop, and people frantically trying to recover lost data. But what exactly happened?
The culprit behind this widespread BSOD outbreak was a critical Windows update that didn’t play well with certain hardware configurations. This update inadvertently caused conflicts with drivers, leading to system instability and those dreaded blue screens. In a matter of hours, forums and social media were flooded with cries for help as users scrambled to find solutions.
But don’t worry! If you’ve ever experienced the BSOD, or if you’re currently staring at one, we’ve got your back. This blog post is your comprehensive guide to understanding, diagnosing, and fixing the Blue Screen of Death. So, grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of BSODs.
What is the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)?
The Blue Screen of Death, often abbreviated as BSOD, is a critical error screen displayed by the Windows operating system when it encounters a severe system error. This error is so significant that it forces Windows to stop completely to prevent further damage. The screen typically displays a blue background with white text detailing the error code and a message explaining the issue.
Why Does the BSOD Happen?
BSODs can be caused by a variety of issues, like:
- Hardware Failures: Defective hardware components such as RAM, hard drives, or power supplies can lead to a BSOD.
- Driver Issues: Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause conflicts, resulting in a system crash.
- Software Conflicts: Certain software applications can interfere with the operating system, leading to instability.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause hardware components to malfunction, triggering a BSOD.
- Corrupted System Files: Essential Windows files that are damaged or corrupted can cause a crash.
- Virus or Malware: Malicious software can corrupt system files and drivers, leading to a BSOD.
How to Diagnose the BSOD

Before diving into the fixes, it’s important to diagnose the root cause of the BSOD. Here are the steps to follow:
- Read the Error Message: When the BSOD occurs, take note of the error message and code displayed on the screen. This information can help identify the cause of the crash.
- Check Recent Changes: Think about any recent changes to your system, such as new software installations, driver updates, or hardware changes. These could be the source of the issue.
- Boot in Safe Mode: Safe Mode starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services. If the BSOD doesn’t occur in Safe Mode, it suggests that a third-party driver or service is causing the problem.
- Use Event Viewer: Windows Event Viewer logs system events, including errors and warnings. Check the logs for entries related to the BSOD to get more details.
- Run Diagnostic Tools: Use built-in Windows tools like Memory Diagnostic Tool and CHKDSK to check for hardware issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing the BSOD
Now that you’ve diagnosed the issue, let’s get to fixing it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you resolve the BSOD:
Update Drivers
Outdated or incompatible drivers are a common cause of BSODs. Here’s how to update them:
Automatic Update:
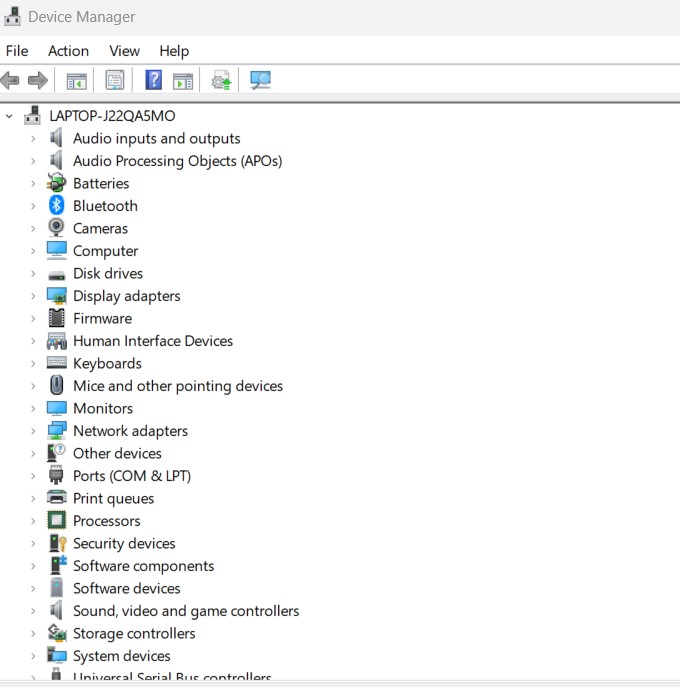
- Open Device Manager (Press Win + X and select Device Manager).
- Right-click on the device with the outdated driver.
- Select Update driver and follow the prompts.
Manual Update:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website for your device.
- Download the latest drivers.
- Install the drivers manually.
Check for Windows Updates
Microsoft regularly releases updates to fix bugs and improve system stability. Make sure your system is up-to-date:
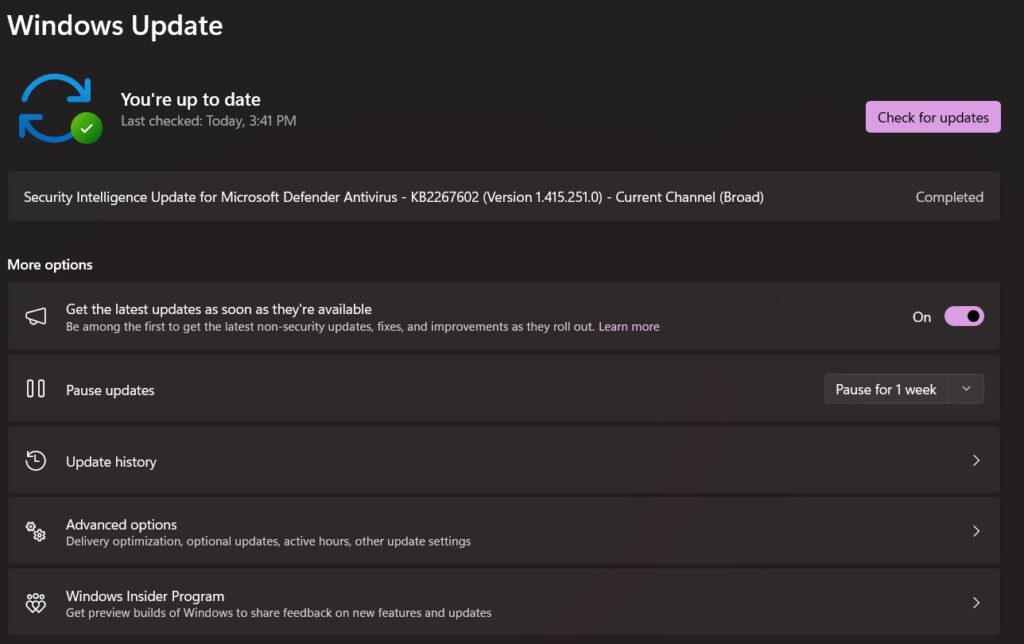
- Open Settings (Press Win + I).
- Go to Update & Security.
- Click Check for updates and install any available updates.
Run System File Checker (SFC) and DISM
Corrupted system files can cause BSODs. Use SFC and DISM to repair them:
System File Checker (SFC):
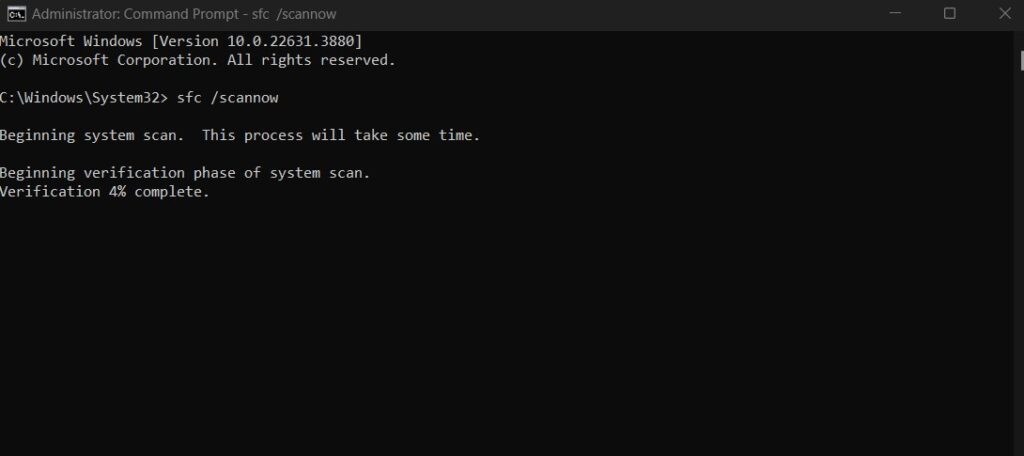
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator (Press Win + X and select Command Prompt (Admin)).
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- Wait for the scan to complete and follow any prompts.
Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM):
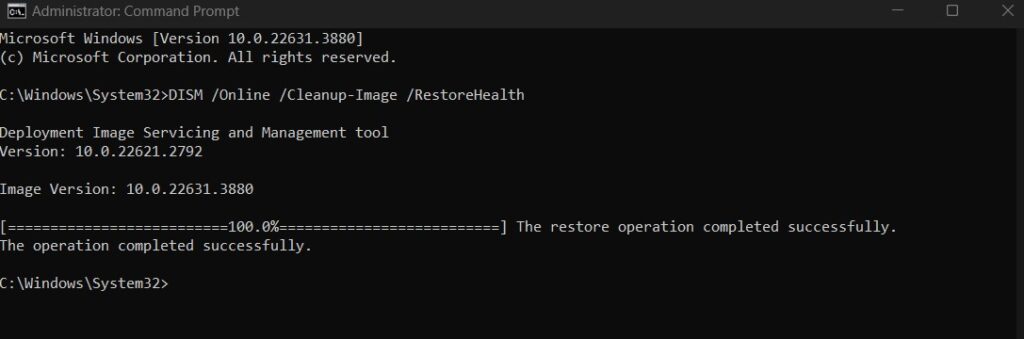
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth and press Enter.
- Wait for the process to complete.
Check for Hardware Issues
Faulty hardware can also trigger BSODs. Here’s how to check for hardware issues:
Memory Diagnostic Tool:
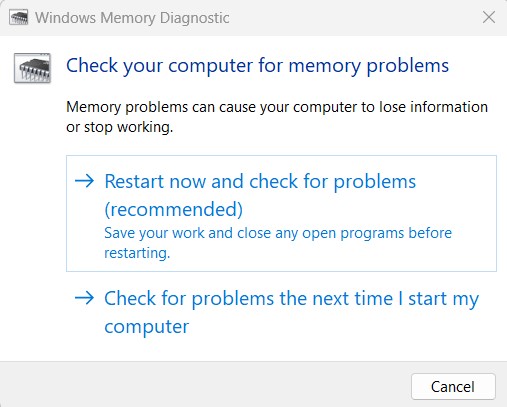
- Press Win + R, type mdsched.exe, and press Enter.
- Choose Restart now and check for problems.
- The system will restart and run the memory diagnostic.
CHKDSK:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator (Admin).
- Type chkdsk /f /r and press Enter.
- Follow the prompts to schedule the check at the next restart.
Uninstall Problematic Software
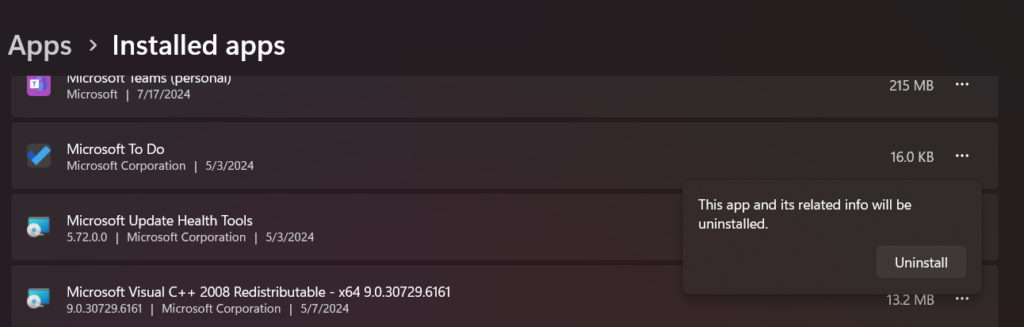
If the BSOD started after installing new software, try uninstalling it:
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to Programs > Programs and Features.
- Find the recently installed software and uninstall it.
Restore System to a Previous Point
If the issue persists, try restoring your system to a previous state:
- Open Control Panel.
- Go to System and Security > System.
- Click System Protection in the left pane.
- Click System Restore and follow the prompts.
Preventing Future BSODs
To minimize the risk of future BSODs, follow these best practices:
Regularly Update Software and Drivers: Keep your operating system, drivers, and software up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
Use Reliable Hardware: Invest in quality hardware components to reduce the likelihood of hardware failures.
Run Antivirus Scans: Regularly scan your system for viruses and malware to prevent malicious software from causing crashes.
Monitor System Temperature: Use software to monitor your system’s temperature and ensure it’s not overheating.
Perform Regular Maintenance: Clean your computer’s internals to prevent dust buildup, which can cause overheating and hardware malfunctions.
When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, the BSOD might persist. In such cases, it’s best to seek professional help. Contact a qualified technician or your device’s manufacturer for assistance. They can perform more in-depth diagnostics and repairs.
FAQs
What should I do if I encounter a BSOD?
First, note the error code on the screen. Restart your computer and see if the issue persists. If it does, try booting in Safe Mode and diagnosing the problem using tools like Event Viewer and diagnostic utilities.
Can outdated drivers cause a BSOD?
Yes, outdated or incompatible drivers are a common cause of BSODs. Keeping your drivers updated can prevent these issues.
How often should I update my system to avoid BSODs?
Regularly check for updates for your operating system and drivers. Aim to update them at least once a month or as soon as new updates are released.
Is it safe to use third-party tools to fix BSODs?
While some third-party tools can be helpful, always download them from reputable sources to avoid malware. Built-in Windows tools are generally safe and effective.
Can overheating cause a BSOD?
Yes, excessive heat can cause hardware components to fail, leading to a BSOD. Ensure your system is well-ventilated and clean of dust.
When should I seek professional help for a BSOD?
If you’ve tried all troubleshooting steps and the BSOD persists, it’s time to seek professional help. Technicians can perform more in-depth diagnostics and repairs.
Conclusion
Experiencing a Blue Screen of Death can be frustrating, but it’s not the end of the world. By understanding the causes, diagnosing the issue, and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can fix the BSOD and get your system back up and running smoothly. Remember, prevention is key, so keep your system updated and maintain it regularly to minimize the risk of future BSODs.
For more in-depth guides and tech support, check out our articles on system performance optimization and troubleshooting on TechKNR.
Discover more from Techknr
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

